Git Cheatsheet

About Git
Git is a distributed version control system that tracks versions of files. It is often used to control source code by programmers who are developing software collaboratively. Design goals of Git include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows — thousands of parallel branches running on different computers.
Table of Contents
- Basic Commands
- Branch Management
- Remote Operations
- Undoing Changes
- Git Configuration
- Advanced Operations
Basic Commands
-
Repository Setup
Terminal window git init # Initialize a new repositorygit clone <url> # Clone a repositorygit status # Check repository status -
Staging Changes
Terminal window git add <file> # Add file to staging areagit add . # Add all changes to staging areagit add -p # Interactive staging -
Committing
Terminal window git commit -m "message" # Commit with messagegit commit -am "message" # Add and commit in one commandgit commit --amend # Modify the last commit
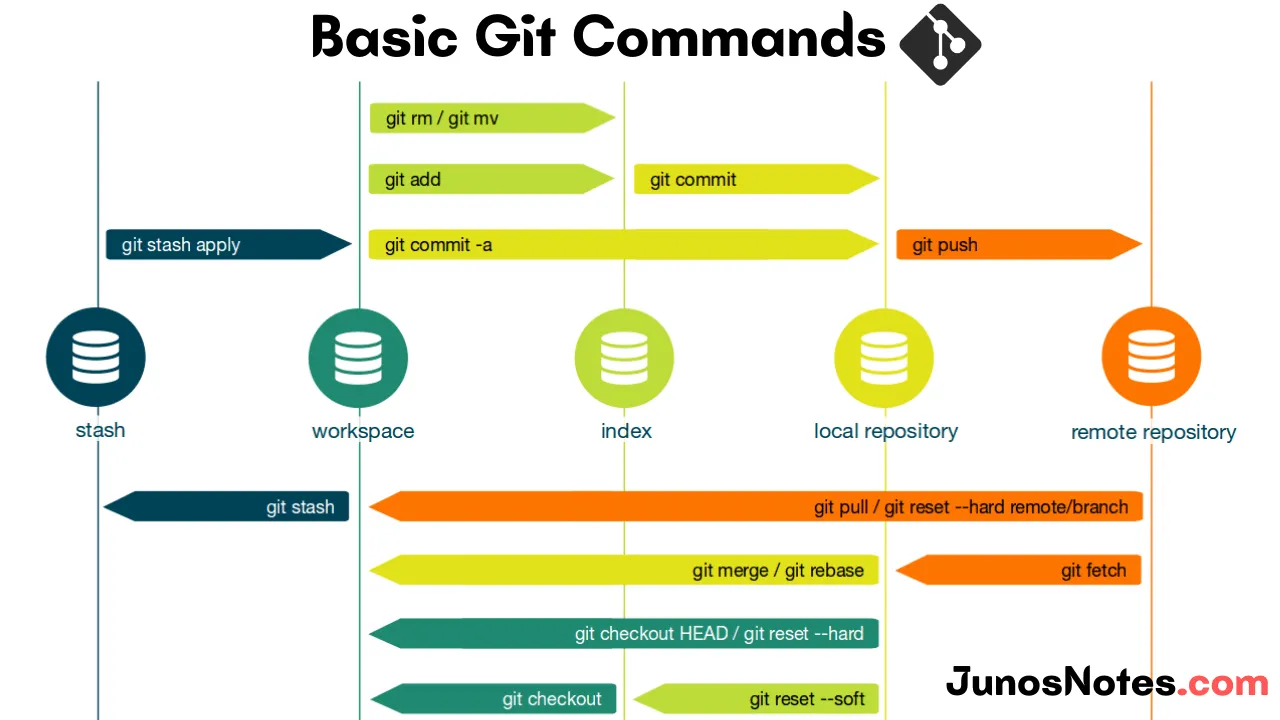
Branch Management
git branch # List branchesgit branch <name> # Create new branchgit checkout <branch> # Switch to branchgit checkout -b <branch> # Create and switch to new branchgit switch <branch> # Switch to branch (new syntax)git switch -c <branch> # Create and switch to new branch (new syntax)git merge <branch> # Merge branch into current branchgit rebase <branch> # Rebase current branch onto anothergit merge --abort # Abort merge in case of conflictsgit rebase --abort # Abort rebaseRemote Operations
git remote add origin <url> # Add remote repositorygit remote -v # List remote repositoriesgit push origin <branch> # Push changes to remotegit pull origin <branch> # Pull changes from remotegit fetch origin # Fetch changes without mergingUndoing Changes
-
Working Directory
Terminal window git checkout -- <file> # Discard changes in working directorygit clean -fd # Remove untracked files and directories -
Staged Changes
Terminal window git reset <file> # Unstage changesgit reset # Unstage all changes -
Commits
Terminal window git reset --soft HEAD~1 # Undo last commit, keep changes stagedgit reset --hard HEAD~1 # Undo last commit and discard changesgit revert <commit> # Create new commit that undoes changes
Git Configuration
git config --global user.name "Your Name"git config --global user.email "your@email.com"git config --global core.editor "code --wait" # Set VS Code as default editorgit config --list # List all configurationsAdvanced Operations
git stash # Stash changesgit stash list # List stashesgit stash pop # Apply and remove latest stashgit stash apply # Apply latest stash without removing itgit log # View commit historygit log --oneline # Compact commit historygit blame <file> # Show who changed what in a filegit reflog # View reference logsgit tag # List tagsgit tag -a v1.0 -m "Version 1.0" # Create annotated taggit push origin --tags # Push tags to remoteBest Practices
- Write clear, descriptive commit messages
- Commit early and often
- Keep branches focused and short-lived
- Pull before pushing to avoid conflicts
- Use
.gitignorefor files that shouldn’t be tracked - Regularly fetch and merge from upstream
- Use meaningful branch names
Common Workflows
-
Feature Branch Workflow
- Create feature branch
- Make changes and commit
- Pull latest main/develop
- Merge or rebase
- Push and create pull request
-
Hotfix Workflow
- Branch from production/main
- Fix issue and commit
- Merge to both main and develop
- Tag release if necessary